Fast Screening and Confirmation of Gamma-Hydroxybutyrate (GHB) in Urine
Maximize your analytical options with this versatile GHB extraction method. No derivatization means faster sample preparation. Extracts are amenable to both liquid injection GC/FID and headspace GC/MS methods.
Gamma-hydroxybutyrate (GHB) and its precursor, gamma-butyrolactone (GBL), are controlled substances associated with drug-facilitated sexual assault. Criminal cases often hinge on lab results, which can include screening urine samples and then quantifying GHB using GC/MS. In its native state, GHB is extremely difficult to chromatograph and must be analyzed as a trimethylsilyl derivative or converted to GBL. The headspace (HS) procedure described here (adapted from an FBI Chemistry Unit method) eliminates time-consuming derivatization [1]. This procedure reduces sample preparation time and minimizes both column contamination from derivatization reagents and contamination from sample matrix caused by liquid injections.
Eliminate Derivatization and Reduce System Contamination
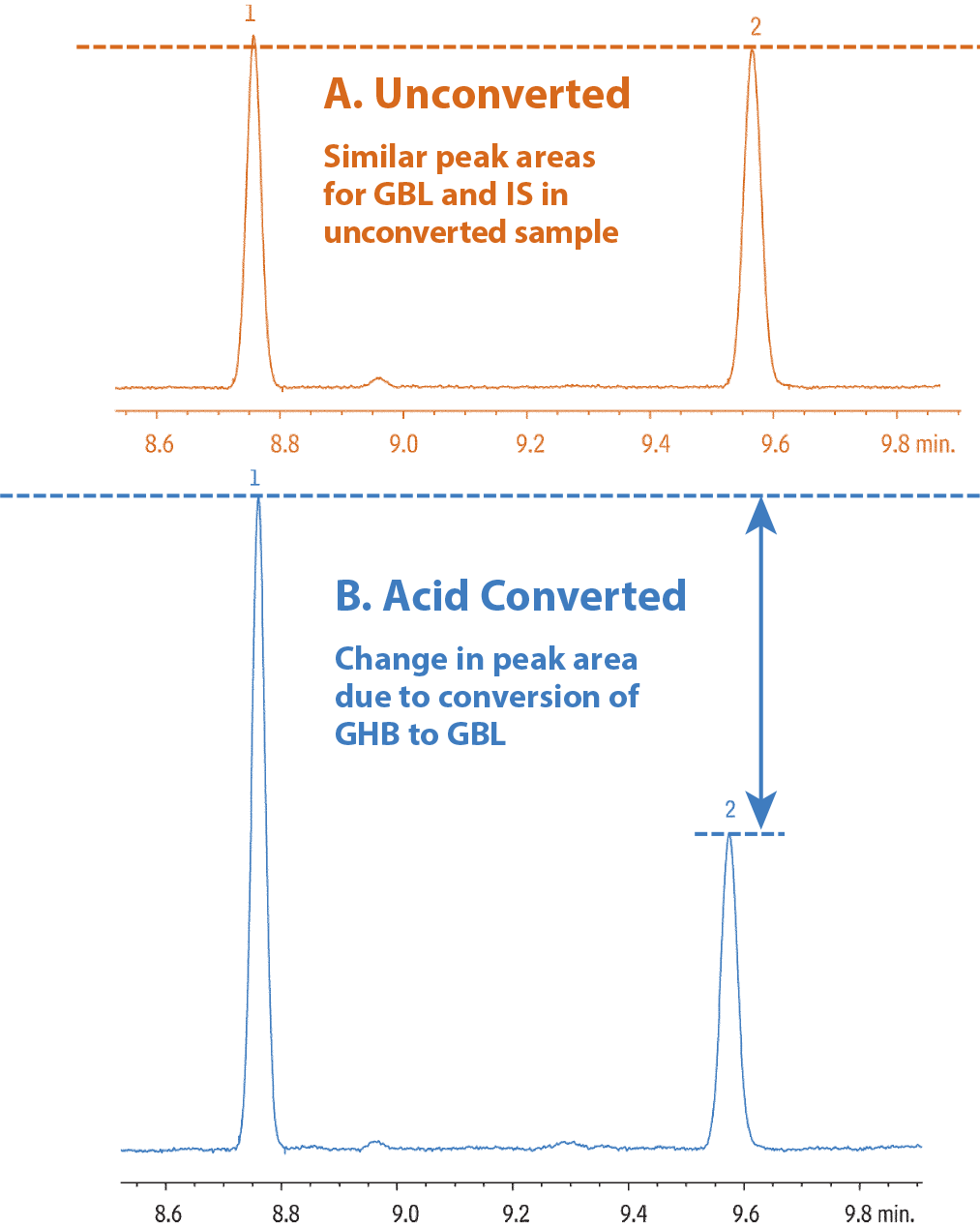
Samples were spiked in urine and extracted according the procedure in Table I, using alpha-methylene-gamma-butyrolactone (AMGB) as an internal standard. GHB is converted to GBL with sulfuric acid, eliminating the need for derivatization (Figure 1). Note the unconverted sample shows comparable levels of GBL and AMGB, whereas GBL levels in the converted sample are significantly higher, due to the conversion of GHB to GBL.
Table I Extraction procedure for GHB and GBL.
|
Reliably Screen Samples Using Existing Blood Alcohol Testing Set-Up
Headspace injections (using the total vaporization technique) of the final urine extracts were screened by GC/FID using an Rtx-BAC1 column in a blood alcohol headspace GC system. This system is commonly used in clinical/forensic labs, eliminating the need for additional equipment. Excellent linear response was obtained from both unconverted (r2 = 0.9992, 10-100 µg/mL 4-point curve) and converted GHB in matrix (r2 = 0.9910, 20-200 µg/mL 4-point curve) with AMBG at 50 μg/mL.
Fast, Definitive Confirmation Analysis by Headspace GC/MS
Positive screening results were quickly confirmed on an Rtx-5MS column by headspace GC/MS; several quantification and qualifier ions were identified for each compound (GBL: 42, 56, 86; AMBG: 40, 68, 98). Again, excellent linearity was achieved (Figure 2) and analysis time was less than 7 minutes (Figure 3).
In summary, the versatile extraction and headspace method shown here saves lab time and minimizes contamination by eliminating the need for derivatization and by reducing matrix effects. Rapid screening is accomplished on commonly used blood alcohol GC columns, allowing labs to reduce costs by using existing equipment. Confirmation testing using the Rtx-5MS column, provides the definitive results needed in court with a fast analysis time of less than 7 minutes.
Figure 1: GHB can be converted to GBL for analysis, saving time by eliminating derivatization.
| Column | Rtx-BAC1, 30 m, 0.32 mm ID, 1.80 µm (cat.# 18003) |
|---|---|
| Standard/Sample | |
| Conc.: | 50 µg/mL GHB, GBL, and AMGB (IS) in urine A: Unconverted B: Converted with sulfuric acid |
| Injection | |
| Inj. Vol.: | 1000 µL headspace-syringe split (split ratio 10:1) |
| Liner: | 1 mm Split |
| Inj. Temp.: | 200 °C |
| Headspace-Syringe | |
| Sample Temp.: | 100 °C |
| Sample Equil. Time: | 10 min |
| Oven | |
| Oven Temp.: | 50 °C (hold 3 min) to 150 °C at 20 °C/min (hold 7 min) |
| Carrier Gas | He, constant flow |
| Flow Rate: | 1.0 mL/min |
| Detector | FID @ 240 °C |
|---|---|
| Make-up Gas Flow Rate: | 40 mL/min |
| Notes | Liner cat.# 20972 was used to produce this chromatogram, but has since been discontinued. For assistance choosing a replacement for this application, contact Restek Technical Service or your local Restek representative. |
Figure 2: GHB (analyzed as GBL) confirmation method calibration curve for headspace GC/MS analysis (10-300 µg/mL in urine).
Figure 3: Confirmation headspace GC/MS analysis of 300 µg/mL converted GHB (analyzed as GBL) standard in urine.

| Column | Rtx-5MS, 30 m, 0.25 mm ID, 0.25 µm (cat.# 12623) |
|---|---|
| Standard/Sample | 300 µg/mL GHB, 50 µg/mL AMGB in urine, converted with sulfuric acid |
| Injection | |
| Inj. Vol.: | 1000 µL headspace-syringe split (split ratio 10:1) |
| Liner: | 1 mm Split |
| Inj. Temp.: | 200 °C |
| Headspace-Syringe | |
| Sample Temp.: | 100 °C |
| Sample Equil. Time: | 10 min |
| Oven | |
| Oven Temp.: | 50 °C (hold 3 min) to 150 °C at 20 °C/min (hold 7 min) |
| Carrier Gas | He, constant flow |
| Flow Rate: | 1.0 mL/min |
| Detector | MS |
|---|---|
| Mode: | Scan |
| Transfer Line Temp.: | 280 °C |
| Ionization Mode: | EI |
| Scan Range: | 20-150 amu |
| Notes | Liner cat.# 20972 was used to produce this chromatogram, but has since been discontinued. For assistance choosing a replacement for this application, contact Restek Technical Service or your local Restek representative. |
References
- M.A. LeBeau, M.A. Montgomery, M.L Miller, S. G. Burmeister, J. Anal. Toxicol. 24 (2000) 421.
