LC-MS/MS Analysis of 58 Antipsychotics and Antidepressants in Human Urine
Featured Application: Mental Health Drugs on Raptor Biphenyl
- Simple sample preparation procedure and fast, 5.5-min total LC cycle time.
- Good chromatographic separation of isobaric compounds.
- Optimized method suitable for quantitative analysis.
Mental health disorders contribute significantly to worldwide morbidity and mortality, a fact reflected in the growing numbers of new antipsychotic and antidepressant drugs entering the market, as well as the rising rate of prescription. These drugs, which are used to treat a wide range of psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, dysthymia, social anxiety disorder, obsessive-compulsive disorder, and chronic pain, have a high potential for abuse. In the forensic setting, detection of these drugs is critical in determining their involvement in intoxications and suicides. In the clinical setting, analysis of antipsychotics and antidepressants in blood or urine is necessary to ensure suitable therapeutic concentration and to monitor patient compliance.
By combining a simple sample preparation procedure and a fast LC-MS/MS analysis of antipsychotics and antidepressants using a Raptor Biphenyl column, a highly specific and accurate method was established for 58 drugs in human urine. Chromatographic carryover, initially problematic, was resolved by rinsing the injector and needle both externally and internally with a 50:50 methanol:DMSO solution. This, coupled with a highly organic initial mobile phase, ensured the chromatographic separation of isobaric compounds (maprotiline and amitriptyline; protriptyline and nortriptyline) needed for quantitative analysis. Under the conditions shown here, a fast, efficient separation was achieved for the simultaneous LC-MS/MS analysis of antipsychotics and antidepressants with a 3.5 minute gradient and a 5.5 minute total LC cycle time.
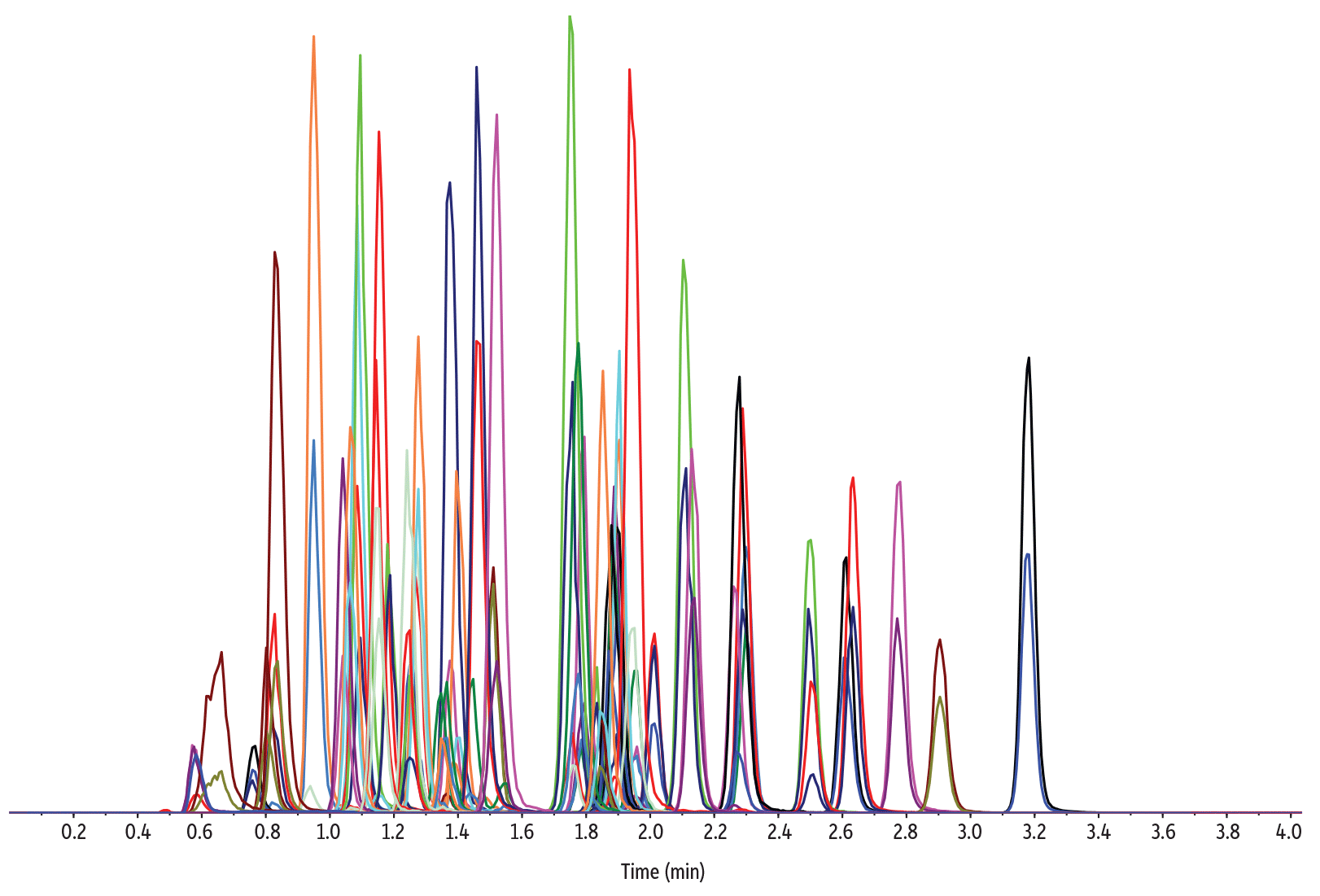
| Peaks | tR (min) | Conc. (ng/mL) | Precursor Ion | Product Ion | Product Ion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Desmethylolanzapine | 0.58 | 2500 | 299.1 | 256.1 | 198.0 |
| 2. | Phenelzine sulfate | 0.59 | 2500 | 137.2 | 105.1 | 77.1 |
| 3. | Olanzapine | 0.65 | 2500 | 313.2 | 256.1 | 198.1 |
| 4. | Lamotrigine | 0.76 | 2500 | 256.0 | 211.1 | 145.0 |
| 5. | Molindone | 0.81 | 2500 | 278.1 | 100.3 | 101.1 |
| 6. | (+/-)-Hydroxybupropion | 0.83 | 2500 | 256.0 | 130.2 | 166.0 |
| 7. | 7-Hydroxyquetiapine | 0.84 | 2500 | 400.3 | 269.0 | 208.0 |
| 8. | Bupropion-D9 (IS) | 0.94 | 200 | 249.2 | 130.9 | - |
| 9. | Bupropion | 0.95 | 2500 | 240.0 | 184.1 | 130.2 |
| 10. | Venlafaxine | 1.04 | 2500 | 278.4 | 260.4 | 121.2 |
| 11. | Reduced haloperidol | 1.07 | 2500 | 378.1 | 359.9 | 109.1 |
| 12. | Milnacipran | 1.09 | 2500 | 247.2 | 100.1 | 129.1 |
| 13. | N-desmethylmirtazapine | 1.10 | 2500 | 252.1 | 195.1 | 209.2 |
| 14. | 9-Hydroxyrisperidone | 1.15 | 2500 | 427.3 | 207.1 | 110.2 |
| 15. | Mirtazapine | 1.16 | 2500 | 266.1 | 195.1 | 72.1 |
| 16. | N-desmethylclozapine | 1.19 | 2500 | 313.0 | 192.1 | 270.0 |
| 17. | Droperidol | 1.24 | 2500 | 380.1 | 122.9 | 165.1 |
| 18. | Clozapine | 1.25 | 2500 | 328.2 | 271.1 | 193.1 |
| 19. | Didesmethyl citalopram | 1.26 | 2500 | 297.1 | 109.1 | 261.9 |
| 20. | N-desmethylcitalopram | 1.27 | 2500 | 311.1 | 109.1 | 262.1 |
| 21. | Escitalopram | 1.28 | 2500 | 325.3 | 109.1 | 261.9 |
| 22. | Fluvoxamine | 1.35 | 2500 | 319.1 | 71.2 | 130.1 |
| 23. | Haloperidol | 1.36 | 2500 | 377.2 | 123.0 | 95.1 |
| 24. | Norfluoxetine | 1.37 | 2500 | 296.3 | 134.3 | 104.9 |
| 25. | Isocarboxazid | 1.38 | 2500 | 232.0 | 91.1 | 65.2 |
| 26. | Fluoxetine | 1.39 | 2500 | 310.1 | 148.0 | 115.1 |
| 27. | Desmethyldoxepin | 1.40 | 2500 | 266.1 | 107.1 | 115.0 |
| 28. | Doxepin | 1.45 | 2500 | 280.1 | 107.2 | 77.1 |
| 29. | Trazodone | 1.46 | 2500 | 372.3 | 176.1 | 148.0 |
| 30. | Oxcarbazepine | 1.51 | 2500 | 253.1 | 180.0 | 208.1 |
| 31. | Risperidone | 1.52 | 2500 | 411.2 | 191.0 | 110.1 |
| 32. | Quetiapine | 1.75 | 2500 | 384.2 | 253.0 | 221.2 |
| 33. | Asenapine | 1.76 | 2500 | 286.2 | 165.1 | 229.1 |
| 34. | Ziprasidone | 1.78 | 2500 | 413.2 | 194.1 | 130.0 |
| 35. | Protriptyline | 1.79 | 2500 | 264.1 | 191.1 | 165.2 |
| 36. | Desipramine | 1.83 | 2500 | 267.1 | 72.1 | 193.1 |
| 37. | Paroxetine | 1.85 | 2500 | 330.2 | 192.2 | 70.1 |
| 38. | Iloperidone | 1.85 | 2500 | 427.1 | 261.1 | 96.1 |
| 39. | Duloxetine | 1.86 | 2500 | 298.1 | 188.2 | 154.1 |
| 40. | Amoxapine | 1.88 | 2500 | 314.2 | 271.0 | 193.1 |
| 41. | Carbamazepine | 1.89 | 2500 | 237.0 | 193.9 | 192.0 |
| 42. | Maprotiline | 1.90 | 2500 | 278.1 | 250.2 | 191.1 |
| 43. | Imipramine | 1.91 | 2500 | 281.1 | 86.2 | 58.1 |
| 44. | Nortriptyline | 1.95 | 2500 | 264.1 | 91.1 | 115.2 |
| 45. | Loxapine | 1.95 | 2500 | 328.1 | 271.1 | 193.0 |
| 46. | Amitriptyline | 2.01 | 2500 | 278.1 | 91.1 | 202.1 |
| 47. | Trimipramine | 2.11 | 2500 | 295.2 | 100.2 | 58.2 |
| 48. | Pimozide | 2.13 | 2500 | 462.1 | 328.0 | 109.1 |
| 49. | Chlorpromazine | 2.26 | 2500 | 319.0 | 86.1 | 178.2 |
| 50. | Dehydro aripiprazole | 2.28 | 2500 | 446.2 | 285.0 | 98.1 |
| 51. | Clomipramine | 2.29 | 2500 | 315.3 | 86.0 | 58.0 |
| 52. | Sertraline | 2.30 | 2500 | 306.2 | 275.1 | 158.9 |
| 53. | Fluphenazine | 2.50 | 2500 | 438.3 | 171.1 | 143.2 |
| 54. | Aripiprazole | 2.51 | 2500 | 448.2 | 285.0 | 176.1 |
| 55. | Perphenazine | 2.61 | 2500 | 404.2 | 171.1 | 143.2 |
| 56. | Trifluoperazine | 2.63 | 2500 | 408.2 | 141.2 | 113.1 |
| 57. | Prochlorperazine | 2.78 | 2500 | 374.1 | 141.0 | 113.1 |
| 58. | Thiothixene | 2.91 | 2500 | 444.2 | 221.2 | 235.0 |
| 59. | Thioridazine | 3.18 | 2500 | 371.2 | 126.1 | 98.1 |
| Column | Raptor Biphenyl (cat.# 9309A5E) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions: | 50 mm x 3.0 mm ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle Size: | 2.7 µm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pore Size: | 90 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Guard Column: | Raptor Biphenyl EXP guard column cartridge 5 mm, 3.0 mm ID, 2.7 µm (cat.# 9309A0253) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Temp.: | 30 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard/Sample | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Conc.: | 2500 ng/mL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Inj. Vol.: | 2 µL | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mobile Phase | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A: | Water, 0.1% formic acid, 5 mM ammonium formate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B: | Methanol, 0.1% formic acid, 5 mM ammonium formate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Detector | MS/MS |
|---|---|
| Ion Mode: | ESI+ |
| Mode: | MRM |
| Instrument | UHPLC |
| Sample Preparation | Drug-free human urine (BioIVT) was fortified with 58 analytes at 2500 ng/mL. Bupropion-D9 was used as the internal standard for quantification of all 58 compounds. The urine sample (50 μL) was mixed with 15 μL of IMCSzyme, 20 μL of reaction buffer, and 10 μL of internal standard solution (1 µg/mL in methanol). Hydrolysis was performed at 45°C (water bath) for 30 minutes, and then 400 µL of acetonitrile was added, vortexed to mix, and centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 10 minutes. The supernatant was diluted 2-fold with water and injected for analysis. |

