GC Analysis of Total Reduced Sulfurs at ppbv Levels
Using an Rxi-1ms Column and Sulfur Chemiluminescence Detection
- Reliable results for ppbv concentrations of highly active sulfur compounds.
- Inert, low bleed column resolves all analytes.
- Column compatible with SCD and other sulfur-specific detectors.
Through the Clean Air Act, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) regulates and limits the emission of toxic air pollutants. The determination of total reduced sulfurs, as required by CFR Title 40, requires the use of methods and equipment capable of providing full resolution as well as high sensitivity. Methods TO-15, TO-16 and TO-16A describe GC procedures that apply to the determination of reduced sulfurs from stationary sources, such as recovery furnaces, lime kilns, smelt dissolving tanks, fuel gas combustion devices, tail gas control units, and others. Method TO-16 specifies detectable concentrations of ppbv levels for dimethyl disulfide, dimethyl sulfide, hydrogen sulfide, and methyl mercaptan. While these methods do not specify the analytical GC column to use, they do state that the column must resolve the sulfur compounds.
Our new 100% dimethylpolysiloxane column, the Rxi-1ms column, provides the ultra-low bleed required for low level detection and quantification of sulfur compounds. Its exceptional inertness allows complete separation of these very reactive compounds, with excellent peak shape, at ppbv levels. When this column is coupled with a sulfur chemiluminescence detector (SCD), the analysis is fast and simple.
For our example analysis, we collected a 20 mL sample of a gaseous mixture of hydrogen sulfide, carbonyl sulfide, methyl mercaptan, ethyl mercaptan, and dimethyl sulfide in helium, using a Sulfinert-treated stainless steel sample loop. We transferred the sample to a SilcoCan air monitoring canister and pressurized the can to 30 psig with dry nitrogen. The Sulfinert passivation treatment on both the sample loop and canister prevented adsorption losses of the highly active sulfur compounds. We introduced a 1 mL aliquot of the diluted gaseous mixture into the Rxi-1ms column via a second Sulfinert-treated stainless-steel sample loop, using helium as a carrier, and analyzed the sample isothermally at 30 °C.
Figure 1 shows the chromatography for the reduced sulfur compounds, demonstrating full resolution in less than 5 minutes. For collecting, storing, and analyzing active sulfur compounds at levels as low as single parts per billion, the performances of Sulfinert passivated containers and transfer systems, and inert Rxi-1ms columns, simply can’t be equaled.
Figure 1: Total resolution of reduced sulfur compounds, in less than 5 minutes, using an Rxi-1ms column.
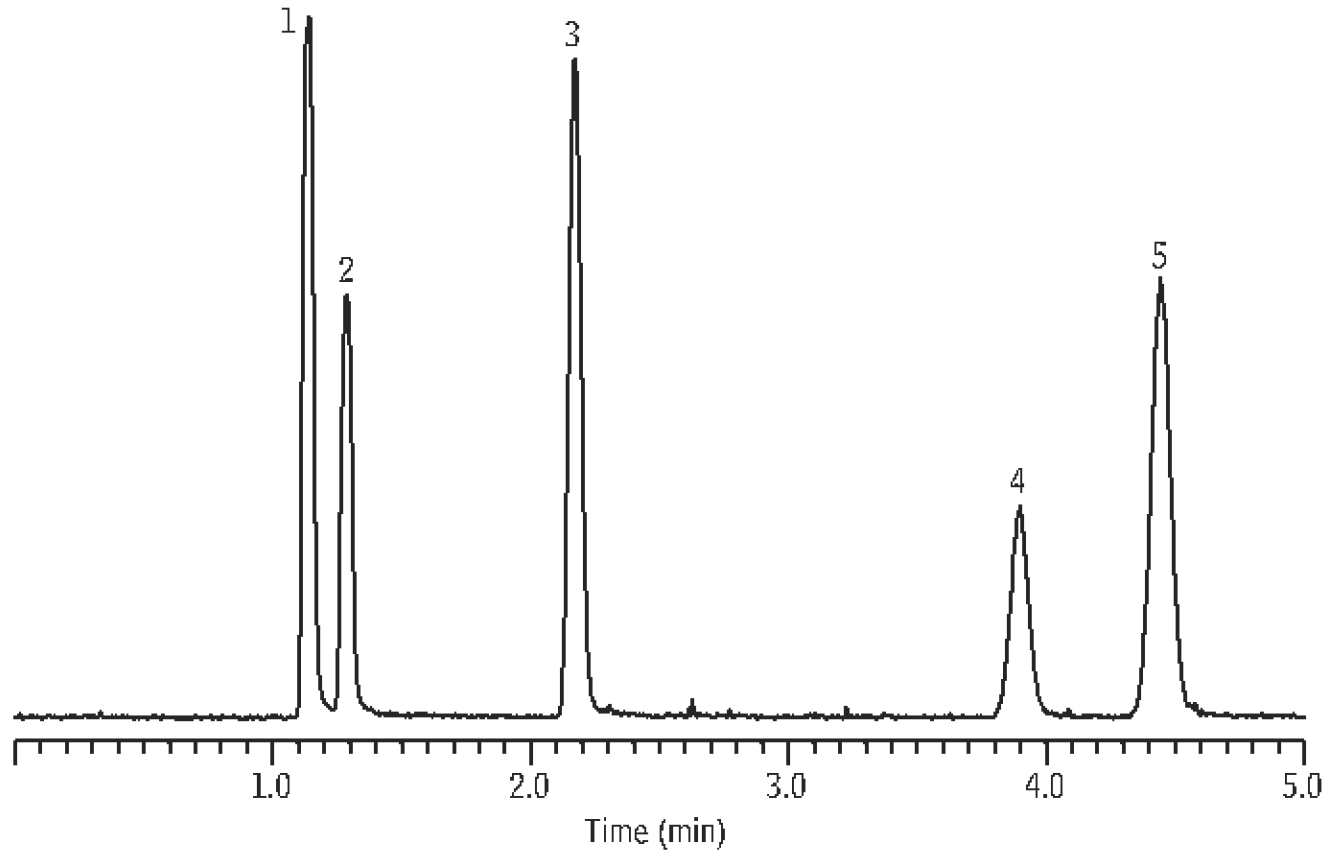
| Peaks | |
|---|---|
| 1. | Hydrogen sulfide |
| 2. | Carbonyl sulfide |
| 3. | Methyl mercaptan |
| 4. | Ethyl mercaptan |
| 5. | Dimethyl sulfide |
| Column | Rxi-1ms, 30 m, 0.32 mm ID, 4.00 µm (cat.# 13396) |
|---|---|
| Standard/Sample | Hydrogen sulfide, carbonyl sulfide, methyl mercaptan, ethyl mercaptan, dimethyl sulfide |
| Diluent: | Helium |
| Conc.: | 100 ppbv |
| Injection | splitless |
| Inj. Temp.: | 30 °C |
| Oven | |
| Oven Temp.: | 30 °C |
| Carrier Gas | He, constant pressure |
| Linear Velocity: | 48 cm/sec @ 30 °C |
| Detector | SCD @ 800 °C |
|---|---|
| Notes | Injection: sample loop (30°C), 1 mL splitless direct Sample Storage and Tansfer: SilcoCan air monitoring canister with Siltek-treated 1/4" valve (cat.# 24182-650); Sulfinert-treated gas sample loop, 1 cc (cat.# 22848); Sulfinert-treated gas sample loop, 10 cc (custom order) |
